Decentralized Identity 3.0 for Digital Government
The intersection of Blockchain and Digital Identity offers a powerful decentralized model for Government services.
 Individually the fields of Digital Identity and Blockchain technologies are both powerful technology trends with a wide spectrum of use case scenarios.
Individually the fields of Digital Identity and Blockchain technologies are both powerful technology trends with a wide spectrum of use case scenarios.
The intersection of the two technologies defines “Identity 3.0”, the foundational infrastructure for the emerging Web 3.0 digital economy and thus a massive growth opportunity.
VentureBeat examines the role that Digital Identity will play in enabling the Web 3.0 economy. They explore example scenarios of Web 3.0 digital business models and the different permutations of Identity architecture that may evolve to facilitate them.
Decentralized Identity
Bain documents a detailed analysis of the landscape: Web3 Could Rewrite the Rules of User Identity, summarizing the trend and how organizations like JPMorgan, Nike, Google, and Disney are pioneering it’s future. As the stack demonstrates the most visible element to end users will be the digital wallets they use to store credentials and other identity services. The Bain article says:
“These wallets act as unified bank accounts and digital passports that have the potential to change how users connect with applications by offering universal sign-in capabilities.”
A commonly agreed architecture principle is that identity will be decentralized; Idenhaus says this will revolutionize Web 3.0. At it’s core is the ‘DID‘ specification from the W3c – Decentralized Identifiers. The Amber Group shares this comprehensive overview of decentralized identity and it’s foundation role for Web 3.0, including documenting the four layers it is comprised of, based on the DIF’s 4-Layer Identity Model.
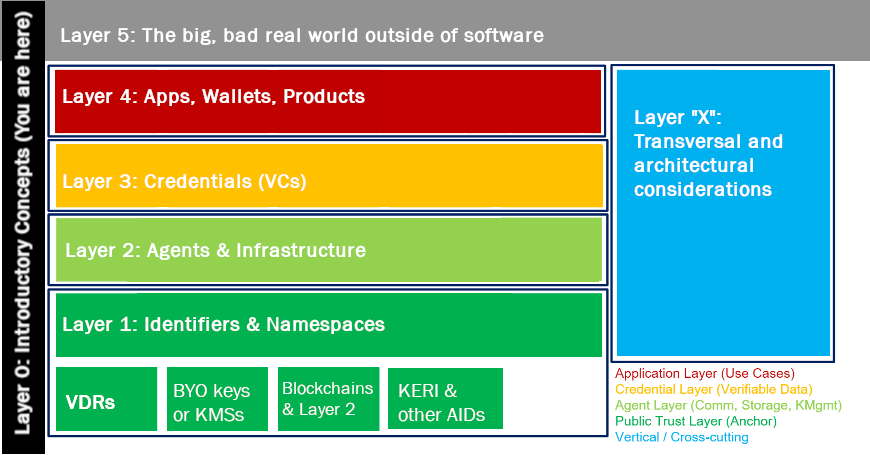
This ecosystem will foster a number of related component part innovations, such as Decentralized PKI and Anonymous Credentials for example. Amber highlights how developments will manifest in the immediate and adapt as it progresses, such as how Goldfinch uses proprietary unique entity checks but aims to leverage decentralized ID solutions when they mature.
Blockchain
It’s also commonly agreed that the Blockchain will play a foundational role in the development of Web 3.0 Identity.
The Global Blockchain Business Council offers this expert panel talk explaining the general role the Blockchain will play in enabling Web 3.0. Speakers from Filecoin, Boson Protocol and Tokens.com describe how Blockchain has the potential to be a driving force as we shift into a web 3.0 world, powering solutions and infrastructures through which we will reimagine the way we envision identity, commerce, and more.
An especially powerful innovation is the role for Blockchain infrastructure to provide an Identity function. For example Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin describes “soulbound tokens” as non-transferable NFTs that can help represent a person’s identity and achievements in Web3.
Another key development is the Ethereum Name Service (ENS), a distributed, open, and extensible naming system based on the Ethereum blockchain. ENS Domains explains:
“ENS has similar goals to DNS, the Internet’s Domain Name Service, but has significantly different architecture due to the capabilities and constraints provided by the Ethereum blockchain. Like DNS, ENS operates on a system of dot-separated hierarchical names called domains, with the owner of a domain having full control over subdomains.
Top-level domains, like ‘.eth’ and ‘.test’, are owned by smart contracts called registrars, which specify rules governing the allocation of their subdomains. Anyone may, by following the rules imposed by these registrar contracts, obtain ownership of a domain for their own use. ENS also supports importing in DNS names already owned by the user for use on ENS.”
We’ll increasingly see innovations emerge that marry these worlds of Identity functions and Blockchain.
 Supercharging Innovation – Building Blocks for Digital Public Infrastructure
Supercharging Innovation – Building Blocks for Digital Public Infrastructure
Writing for TechUK Wiggin’s Kristian Hall and Marcus Bagnall propose that the UK could lead this field of innovation.
They describe how NFT verification would work by associating crucial identity information with digital tokens, thereby providing users with a trustworthy and tamper-proof representation of their online identity, and blockchain smart contracts could ensure secure, autonomous data sharing.




