National Blockchain Roadmaps: Foundations for a 21st Century Digital Economy
National Blockchain Roadmaps serve as a blueprint for countries to build a resilient and innovative digital economy in the 21st century.
 Digital Identity and Blockchain technologies provide the common building blocks for digital nation infrastructure.
Digital Identity and Blockchain technologies provide the common building blocks for digital nation infrastructure.
They provide foundation components that applications can build upon to achieve heightened levels of streamlined user experience flows and data integration, security and authenticity.
Countries including the UK, Scotland, Australia, Malaysia and India have developed National Blockchain Roadmaps. By leveraging blockchain technology, countries can:
- Enhance Data Security and Privacy.
- Improve Transparency and Accountability.
- Streamline Business Processes.
- Enable Seamless Cross-Border Transactions.
- Foster Innovation and Entrepreneurship.
- Empower Citizens with Digital Identities.
As countries continue to develop and implement National Blockchain Roadmaps, they are laying the foundation for a digital economy that is inclusive, efficient, and secure.
Digital Economy
Countries collaborate with industry experts, academia, and blockchain developers to create a comprehensive roadmap that aligns with the country’s economic goals and technological capabilities. India describes:
“To create trusted digital platforms through shared Blockchain infrastructure; promoting research and development, innovation, technology and application development; and facilitating state of the art, transparent, secure and trusted digital service delivery to citizens and businesses, thus making India a global leader in Blockchain Technology.”
National Blockchain Roadmaps outline specific focus areas such as regulatory frameworks, infrastructure development, talent acquisition, and use cases for blockchain implementation in key sectors. Malaysia defines that:
“Blockchains will be a critical drive factor in Malaysia’s digital transformation, which can be effectively undertaken and managed through five ecosystem building blocks, in particular Collaboration, Amplifier, Talent, Legal & Governance, and Enablers, abbreviated as CATLE.”
Technology
Roadmaps explain the core technologies involved in building national Blockchain capabilities:
Blockchain is an amalgamation of various innovations, with a clear business value. Blockchain enables a shared ledger among the various parties involved in business transactions, which acts as the single source of truth. Blockchain eliminates the need for a central entity to validate the transactions.
Blockchain, a distributed ledger technology, enables a layer of trust and eliminates the need for a third party to validate the transactions. Data and transactions stored in blocks of Blockchain are secured against tampering using cryptographic hash algorithms. Blocks are linked with each other with proper security using hash function. This leads to a Blockchain, which is a distributed ledger stored at various nodes in the network. Each block contains details of transactions, hash of the previous block, timestamp etc.
Commercial Models
Roadmaps identify the possible commercialization scenarios and business models. For example India describes the opportunity for ‘Blockchain as a Service’:
“National Blockchain Framework would be used for development and large-scale hosting of Blockchain applications in different areas such as agriculture supply chain, electronic health records, education certificate chain, drug supply chain, etc. This infrastructure will be used for providing Blockchain-as-a-Service.”
Use Cases
Importantly these roadmaps document a rich landscape of potential use cases where these technologies can be applied, each offering a considerable entrepreneurial opportunity for building ventures in these specific segments. They also list examples of these ventures already in progress.
Education
Blockchain in education offers tamper-proof digital records for qualifications, streamlining storage, sharing, and transfer of academic credentials while preventing fraud. It improves data management with a secure, decentralized database for educational records.
Decentralised learning platforms enable peer-to-peer learning and credentialing, fostering a flexible, merit-based system. Additionally, blockchain allows institutions to track funding sources transparently, ensuring effective resource allocation.
Example Venture: QualiChain
QualiChain uses Blockchain technology to decentralise lifelong learning and provide lifelong learners with transparent and immutable educational accreditation. At the same time, lifelong learners are provided with personalised recommendations that help them reach their personal and professional learning goals.
Media
Blockchain technology holds great potential to transform the Media and Entertainment Industry, with companies like Delic, Blockchain Comics, and Dopamine Games Limited from Scotland poised to capitalize on this trend. Platforms like Delic’s and VAULT’s offer new revenue streams, while BetDEX’s decentralised sports betting attracts users and benefits content creators.
Blockchain enhances fan engagement via tokenization, improves advertising transparency, and supports decentralised social networks. These applications revolutionise content creation, distribution, and consumption, empowering creators, streamlining processes, and promoting transparency.
Crypto Banking
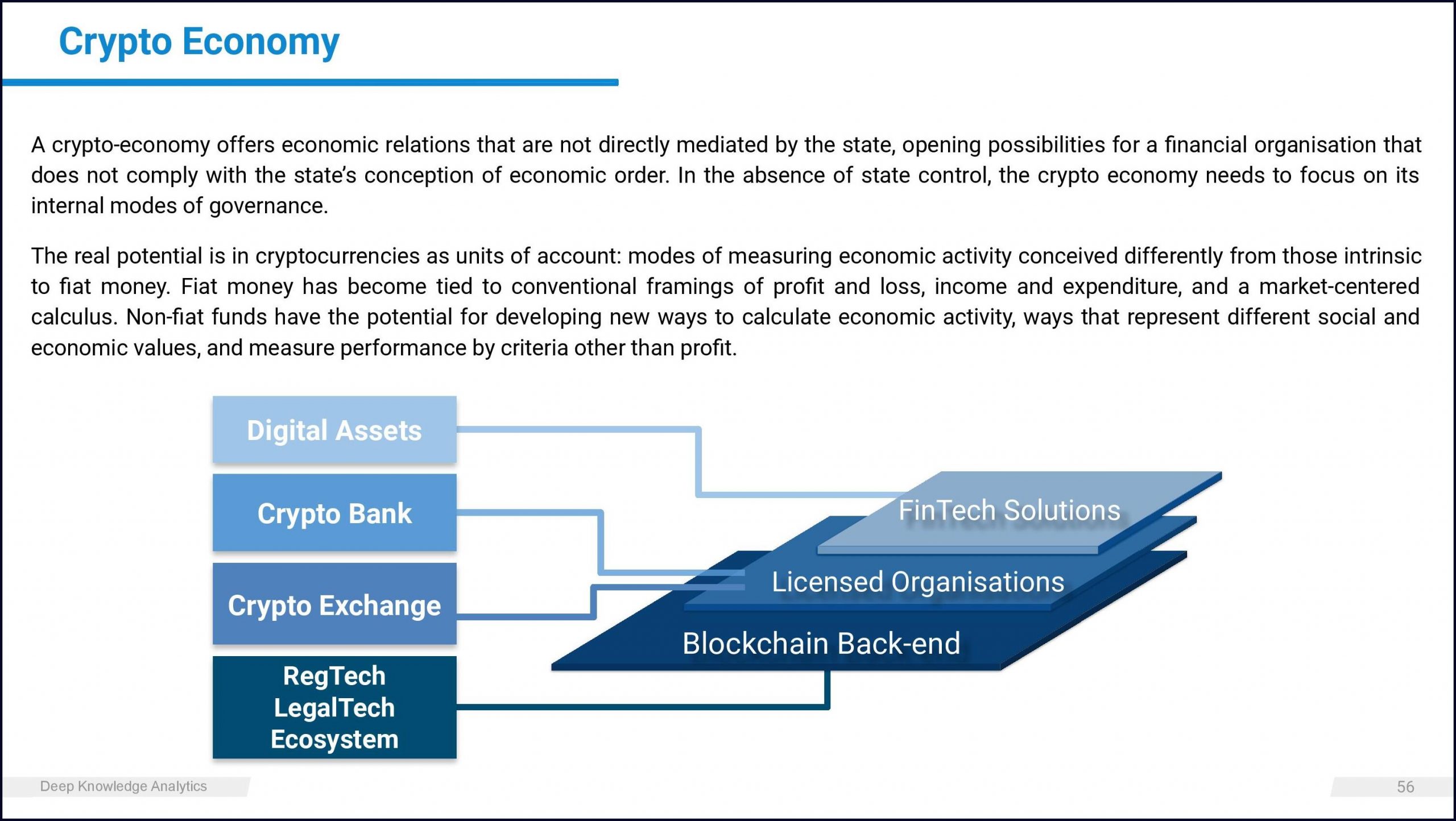
A crypto-economy offers economic relations that are not directly mediated by the state, opening possibilities for a financial organisation that does not comply with the state’s conception of economic order. In the absence of state control, the crypto economy needs to focus on its internal modes of governance. The real potential is in cryptocurrencies as units of account: modes of measuring economic activity conceived differently from those intrinsic to fiat money.
Fiat money has become tied to conventional framings of profit and loss, income and expenditure, and a market-centered calculus. Non-fiat funds have the potential for developing new ways to calculate economic activity, ways that represent different social and economic values, and measure performance by criteria other than profit.